Below is an excerpt from ISS-Corporate’s recently released paper “Are Supermajority Votes Headed for Extinction?” The full paper is available for download from the ISS-Corporate online library.
Shareholder proposals to eliminate supermajority vote requirements are soaring among the biggest listed U.S. companies, a sign that investors feel more well-represented in businesses that make decisions based on a simple majority. The percentage of S&P 500 companies still employing supermajority rules has declined to just over one third, meaning those retaining the practice increasingly look like outliers and may face more scrutiny and pressure to change.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Shareholder proposals seeking to reduce supermajority vote requirements are the most frequently voted proposal type in 2024 so far, growing fivefold over the year earlier.
- 81% of the shareholder proposals to either reduce or eliminate supermajority vote requirements passed thus far in 2024.
- Management proposals to reduce or eliminate supermajority vote requirements have received median support of 80% year to date.
- As shareholders continue to push against supermajority vote requirements, we expect more companies to put these proposals on ballot.
- 56% of Russell 3000 companies require supermajority votes to amend their charter and/or bylaws, while only 35% of S&P 500 companies do the same.
- Shareholders perceive supermajority vote requirements as a governance risk. Companies requiring a supermajority should prepare to receive shareholder proposals aiming for a change.
Supermajority vote requirements often function as de facto barriers to amending a company’s bylaws and/or charters, limiting the shareholders’ ability to make meaningful changes.
In general terms, proposals to reduce supermajority thresholds, whether put forth by management or shareholders, urge the board to eliminate any vote requirement exceeding a simple majority. ISS-Corporate’s Kosmas Papadopoulos [1] recalls a Tesla vote in 2019 in which two proposals to make the company’s governance practices more shareholder-friendly failed despite each proposal receiving over 99.5% of the votes cast. In order to pass, these proposals required support from at least two-thirds of all outstanding shares, yet only 52% of the company’s share capital was represented at the meeting, making it impossible for the proposals to pass.
According to analysis conducted by ISS-Corporate, 56% of companies in the Russell 3000 require a supermajority vote to approve amendments to their charter or bylaws.
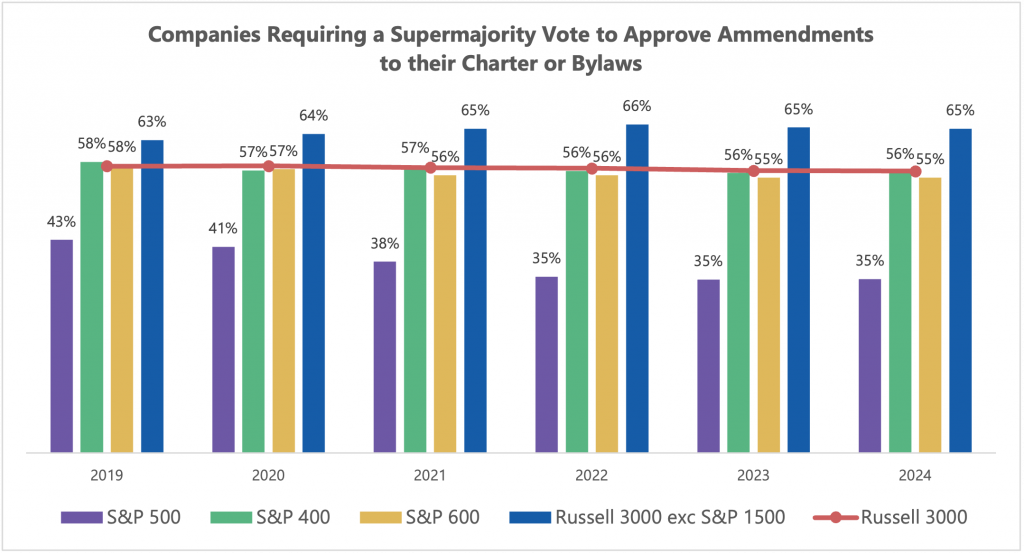
Source: ISS-Corporate QualityScore
Although year-to-year changes are modest, the difference between small cap and large cap companies is significant. Just over one third of S&P 500 companies require supermajority votes, with the total dropping from 43% in 2019 to 35% at the present time. Meanwhile 65% of issuers in the Russell 3000 excluding the S&P 1500 require supermajority votes, little changed from 2019.
[1] Papadopoulos, K. 2019 ISS Analytics, Papadopoulos, K. 2019 ISS Analytics, An Overview of Vote Requirements at U.S. Meetings. Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance, accessed 05/22/2024
By:
Sandra Herrera Lopez, Vice President, Data Analytics Research, ISS-Corporate
Stephanie Hollinger, Vice President, Compensation & Governance Advisory, ISS-Corporate




