Below is an excerpt from ISS-Corporate’s recently released article “Global Interest in ISSB Standards Rises Amid EU Uncertainty”. The full article is available on the ISS-Corporate online library.
Twenty countries have adopted the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) S1 and S2 into their jurisdictional reporting frameworks. A similar number of countries are also undergoing consultation to finalize ISSB adoption roadmaps for sustainability reporting. According to ISSB Chair Emmanuel Faber, jurisdictions progressing toward ISSB adoption collectively represent over 60% of total global GDP.
ISSB and CSRD Adoption
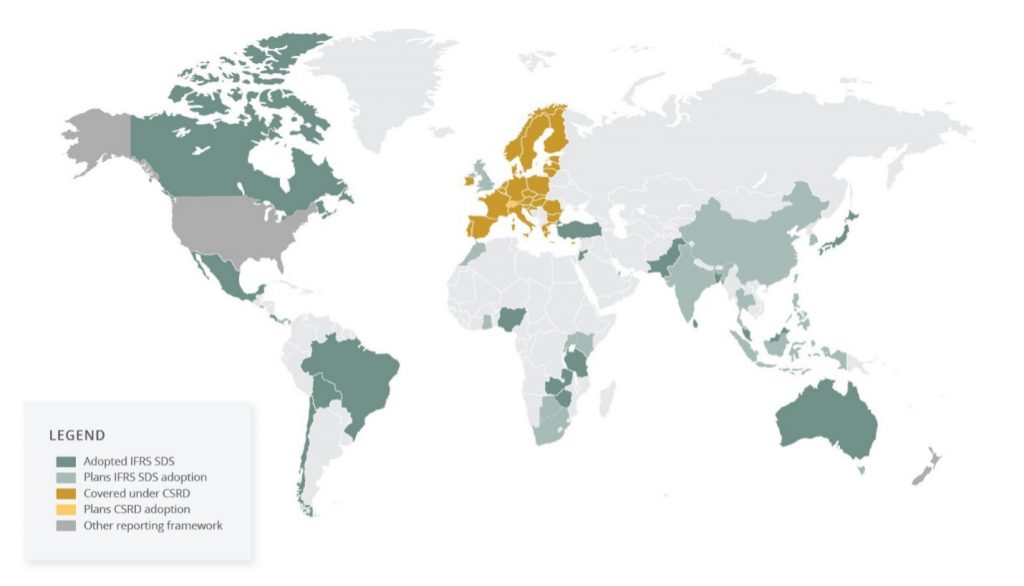
The global adoption of the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards (SDS) takes on added significance amid the EU’s proposed Omnibus package, which is expected to scale back the scope of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
The IFRS SDS are built on the four pillars of the Taskforce on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) – governance, strategy, risk management, metrics and targets. The framework currently includes two standards: IFRS S1 – General Requirements for Disclosure of Sustainability-related Financial Information – and IFRS S2 – Climate-related Disclosures. Three key concepts underpin both standards, guiding how entities should prepare, evaluate, and report sustainability information. These are:
- Financial materiality – information is material if omitting, misstating, or obscuring it could reasonably be expected to influence the decisions of the primary users of general-purpose financial reporting.
- Connectivity – sustainability-related financial disclosures should connect directly to an entity’s financial statements.
- Proportionality – entities should use all reasonable and supportable information that is available at the reporting date without undue cost of effort, where reporting should be commensurate with the skills, capabilities, and resources that are available to the company.
Central to the standards are the needs of existing and potential investors, with a focus on sustainability-related risks and opportunities that could reasonably be expected to affect the cash flow, access to finance, or cost of capital for an entity. In 2023, the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) endorsed the inaugural standards, reinforcing their credibility. This endorsement, along with the flexibly for jurisdictions to adopt the standards in phases, has led several national securities regulators to move forward with implementation. As the ISSB looks to establish a global baseline for sustainability disclosures, adoption continues to expand across jurisdictions.
By:
Guy Lewis, Senior Associate, Sustainability Advisory, ISS-Corporate




