Introduction
This is the second article in a series of three to be published on the topic of the Sustainability Bond Rating at ISS ESG.
As highlighted in our first article ‘The Sustainability Bond Rating and Current GSSS Market,’ the sustainable debt market has seen significant growth, reaching $5.7 trillion in 2024, with green bonds accounting for 60% of new issuances.
ISS ESG has been laying the foundations for a Sustainability Bond Rating (SBR), with the product launch scheduled for April 2025. A new dedicated SBR team of analysts, headed by experienced management, will evaluate the sustainability performance of Green, Social, Sustainability, Sustainability-Linked (GSSS, or labelled) bonds, Transition bonds, and Hybrid bonds through a comprehensive proprietary rating methodology, covering on average 150 indicators per issuance type.
The new SBR will provide a comprehensive assessment of a labelled bond’s ESG performance, answering the currently unaddressed need for asset-level data and assessments. Further, the ISS ESG’s SBR methodology takes into consideration globally accepted frameworks and standards applicable to labelled fixed income instruments, supporting investors to make informed decisions on global issuances, regardless of type of issuer, trading markets, or local and regional regulatory initiatives.
This article describes the mechanics of assessing a Green, Social, Sustainable, Sustainability-Linked (GSSS) bond and examines the SBR’s strengths as well as a hypothetical use case for investors.
Methodological Foundations
The SBR methodology builds on bond labelling standards developed by the International Capital Market Association (ICMA), as well as other international normative frameworks. The ICMA Principles have introduced guidelines for GSSS Bonds for external reviewers. These guidelines are voluntary in nature and provide a strong framework to aid in the issuance of GSSS Bonds. SBR also draws on frameworks such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), to assess a bond’s impact on environmental and social issues, and the EU Taxonomy, to determine an issuance’s potential level of alignment with the European environmental objectives.
What Sets SBR Apart in the Current Market
For labelled bonds, SBR provides both a robust rating system and raw data delivery, setting a new standard in the market. By offering a comprehensive assessment of bonds alongside detailed raw data, ISS ESG expects to empower clients with flexibility – clients can rely on the rating’s outputs for decision-making purposes or leverage the raw data to carry out bespoke analysis. This dual approach supports a broad spectrum of uses, from aiding investment decisions to regulatory compliance.
Distinct features of SBR include issuance-level assessment, annual reviews, and ratings that are comparable across different bond types.
Detailed Issuance-Level Assessment
ISS ESG acknowledges the significance of conducting assessments at the issuance level. Rather than building an assessment on general elements from the issuer’s activities and performance, an issuance-level assessment allows investors to draw key insights on the material ESG risks and opportunities of a labelled bond. SBR implements separate methodologies and approaches for Use of Proceeds (UoP) bonds and Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLBs).
For UoP bonds, the bond’s impact assessment includes assessment of the bond’s project categories vis-à-vis the U.N. SDGs to offer a detailed view of the impact on specific sustainability goals. Moreover, an Environmental & Social risk assessment provides critical insights into material ESG risks. Disclosure of EU Taxonomy and Climate data at the bond level is also part of the dataset.
For SLBs, the assessment is tailored to the issuer’s selected Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Sustainability Performance Targets (SPTs). Also, the integration of bond financial data helps to evaluate the financial materiality of sustainability-linked commitments, ensuring a holistic view of an issuer’s sustainability objectives and risk exposure.
Annual Review and Updates
SBR incorporates an annual review of the covered universe. These updates reflect the latest available data and any changes in the rating based on the updated disclosure by the issuer. This enhances transparency and provides a more accurate representation of a bond’s performance.
Rating Outputs and Scores
SBR implements an established rating scale used across the ISS ESG Corporate Rating and ESG Country Rating. This system utilizes both a numeric scale from 1 to 4, where 1 represents the lowest rating and 4 signifies the highest, and an alphabetic scale ranging from D- to A+. This harmonized approach enhances comparability across different bond types, making it more straightforward for clients to integrate the rating system into their overall sustainability and investment strategies.
Figure 1: SBR Alphabetic and Numeric Rating Scale
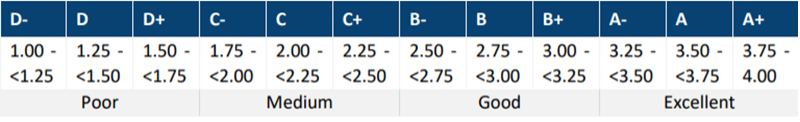
Source: ISS ESG
How SBR Differs from Second Party Opinions
The current market for GSSS or Transition and Hybrid bonds solutions offers a diverse range of products and services aimed at facilitating issuance (i.e., pre-issuance), analysis and impact measurement (i.e., post-issuance), index solutions, etc. At ISS ESG, the Sustainability Bond Rating solution is a post-issuance assessment of the bonds, focusing on the publicly available data from the issuer to help investors make an informed decision.
As displayed in Table 1, ISS ESG’s SBR differs from Second Party Opinions (SPOs) in the nature and coverage of the solution, the delivery mode, and the benefits for investors.
Table 1: Comparison of ISS ESG’s Sustainability Bond Rating to Second Party Opinion
| ISS ESG’s Sustainability Bond Rating | Second Party Opinion | |
| Nature of the solution | Post-issuance assessment of individual instruments, offering a variety of data points as well as an overall rating based on a defined scoring system. SBRs are not commissioned by issuers. | Pre-issuance independent assessment of the quality of an individual issuer’s financing framework, commissioned by the issuer. |
| Coverage | Intended to reach full coverage of the labelled bond market. | Performed on an ad hoc basis. |
| Delivery mode | Delivered in the form of a data feed constituted of the overall rating score and a comprehensive set of underlying data points. | Delivered in the form of a report outlining the results of the evaluation process. |
| Benefit for investors | Allows investors to compare sustainability characteristics of a labelled bonds universe and can assist in selecting investments as well as with reporting. | Offers investors an in-depth analysis of an individual financing framework in line with market guidelines. |
| Update cycle | Annually updated over the life of the bond. | One-time assessment covering all bonds issued under a financing framework. |
Source: ISS ESG
Key Advantages of ISS ESG’s Sustainability Bond Rating
Because of its distinctive characteristics, using the SBR offers several key advantages (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Key Advantages Offered by the Sustainability Bond Rating

Source: ISS ESG
Enhanced Transparency & Credibility: Transparent and detailed analysis helps to build investor confidence, assuring that the proceeds will be used for projects with genuine environmental and social benefits. It helps distinguish the bond as credible in an increasingly competitive and growing market.
Alignment with Global Standards: The SBR ensures that the bond meets the necessary criteria and aligns with global standards for labelled instruments. This alignment can improve the attractiveness of the bond for institutional investors, who are bound by strict mandates regarding the sustainability criteria they must meet.
Greenwashing Risk Mitigation & Reputational Protection: By assessing a bond’s alignment with established frameworks and standards, the risk of greenwashing that investors might potentially face is mitigated. Assessing such alignment also helps avoid potential legal or regulatory issues by ensuring compliance with international sustainability and reporting standards.
Performance Monitoring & Impact Measurement: As bond proceeds are allocated to different environmental and social projects over time, SBR helps in tracking bonds’ material environmental and social risks and their impact on the SDGs.
Regulatory Compliance & Policy Support: The SBR can help investors to comply with disclosure requirements set out in current and upcoming regulations such as the EU Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation and other climate policies. Additionally, SBR would proactively incorporate any upcoming regulatory developments such as the recent EU Green Bond Standard.
A Hypothetical Case Study
An energy generation company issued a green bond with an amount of $500 million in March 2023, stating that the proceeds are to be distributed as per the issuer’s 2022 Green Finance Framework. The SBR would evaluate several different dimensions of this green bond.
“Alignment with International Standards” Dimension
SBR assesses alignment with global standards such as the ICMA principles. For greater transparency and comparability of rated instruments, SBR further evaluates if bond proceeds are also used for refinancing projects. In this case, SBR provides data on the bond’s alignment with the ICMA Green Bond Principles, the inclusion of an SPO covering the financing framework, and the presence of a provision that explicitly allows for project refinancing, with a lookback period of up to 36 months.
In consequence, the dimension garners a score of 2.7, reflecting good performance: while the bond is ICMA-aligned and includes an external review, a shorter lookback period would lead to a higher score, in line with best practices in the market. Evolution in issuer disclosures is captured in the yearly update cycle.
“Environmental and Social Impact Assessment” Dimension
Another dimension of the rating is the “Environmental and Social Impact Assessment,” where the contribution of bond proceeds towards positive environmental or social outcomes and mitigation of greenwashing risk is considered. In this respect, SBR not only assesses the impact of allocated proceeds on SDGs but also assesses the issuers’ commitments towards managing environmental or social risks during the lifecycle of the bond.
In this case, the bond’s framework mentions three eligible categories for proceeds allocation: renewable energy, green buildings, and clean transportation. SBR takes into consideration the point in time where bond’s proceeds are allocated among eligible categories as follows:
In 2023, when the bond was issued, the issuer had not allocated any of the proceeds into projects and there was no accompanying allocation and impact report. In 2024, 100% of the proceeds were allocated, with 70% in wind energy projects and 30% in green buildings.
Table 2: Allocation Timeline
| Timeline | Allocation |
| 2023 | No Disclosed Allocation |
| 2024 | 70% – Wind Energy 30% – Green Building |
Source: ISS ESG
An Impact Assessment for this bond would be conducted every year based on the allocation of proceeds into the projects and whether funded projects are revenue-generating (products or services with direct environmental or social impact) or for operational improvement (issuer’s business practices). To this effect, the positive/negative impact of each project category is determined based on a five-point scale, in line with the SBR rating scale. Tables 3-4 present the bond’s SDG impact assessment, by year:
Table 3: Year 1 (2023): No Allocation, Hence Total Proceeds Are Estimated to Be Allocated to All Three Eligible Categories Equally
| Name of project category | Type of project category | Allocated percentage of the overall value | Project category score | SDG 7 | SDG 11 | SDG 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy generation based on wind | Revenue Generating | 33.3% | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Buildings certified to a comprehensive sustainable building standard | Operational Improvement | 33.3% | 3 | 3 | ||
| Electric vehicles | Operational Improvement | 33.4% | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| SDG Impact Assessment | 3.33 |
Table 4: Year 2 (2024): 70% Is Allocated to a Wind Energy Project and 30% to Green Building
| Name of project category | Type of project category | Allocated percentage of the overall value | Project category score | SDG 7 | SDG 11 | SDG 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy generation based on wind | Revenue Generating | 70% | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Buildings certified to a comprehensive sustainable building standard | Operational Improvement | 30% | 3 | 3 | ||
| SDG Impact Assessment | 3.7 |
Note: Based on the issuer’s allocation report for 2024, no proceeds were allocated to the “Electric Vehicle” category.
Source: ISS ESG
As shown in Tables 3 and 4, the availability of an allocation report from the issuer leads to a change in impact scores over the years and ultimately affects the bond’s overall score.
To further aid with performance monitoring and impact measurement of such labelled bonds, an assessment of the issuer’s management of environmental and social risks is conducted based on disclosures made in publicly available documents about the environmental and social standards (related to Water, Biodiversity, Human Rights, etc.) and the issuer’s level of commitment. This is assessed every year until full proceed allocation.
For instance, the assessment of business ethics practices in the management of financed projects takes into consideration the adoption of commitments to abide by international frameworks, such as the OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises. Table 5 below shows the differing impact on the Business Ethics topic score between Year 1, when the issuer had not communicated its commitment to abide by the OECD Guidelines, and Year 2, when such commitment was disclosed in the allocation report:
Table 5: Evolution of the Business Ethics Topic Score
| Topic: Business Ethics | Score |
| Year 1 (before commitment to OECD Guidelines) | 1 |
| Year 2 (after commitment to OECD Guidelines) | 4 |
Source: ISS ESG
“Issuer’s Sustainability Strategy” Dimension
Finally, by analyzing issuer-level sustainability commitments and practices, SBR provides an opinion on the bond’s alignment with the issuer’s overall sustainability strategy and its potential contribution towards achievement of the issuer’s targets. These factors constitute the third dimension of the rating, “Issuer’s Sustainability Strategy.” In this case study, the eligible project categories are in line with the energy generation company’s path towards transitioning to renewable energy sources.
Importance for Market Participants
The labelled debt market has witnessed tremendous growth in the last decade. The market landscape remains dynamic, with the implementation of various sustainable finance taxonomies promoting green and transition finance instruments. However, a lack of standardized ESG assessments in the market has led to an increasing demand for issuance-specific assessments for investors.
With the Sustainability Bond Rating, ISS ESG caters to fixed income investors’ need for data and analysis that can inform both investment decision-making and reporting for regulatory compliance. Data for this rating is derived through a rigorous process that includes multiple sources and robust quality control measures. This process ensures that the rating can be relied upon by financial market participants and other stakeholders as a reliable source of information on a debt instrument’s sustainability performance.
The availability of this data provides greater transparency across the market and can bring disaggregated pre-issuance and post-issuance information under one umbrella to effectively aid in steering capital towards environmentally sustainable economic activities while reducing greenwashing risk.
Explore ISS ESG solutions mentioned in this report:
- Access to global data on country-level ESG performance is a key element both in the management of fixed income portfolios and in understanding risks for equity investors with exposure to emerging markets. Extend your ESG intelligence using the ISS ESG Country Rating and ISS ESG Country Controversy Assessments.
- Identify ESG risks and seize investment opportunities with the ISS ESG Corporate Rating.
- Financial market participants across the world face increasing transparency and disclosure requirements regarding their investments and investment decision-making processes. Let the deep and long-standing expertise of the ISS ESG Regulatory Solutions team help you navigate the complexities of global ESG regulations.
- Use ISS ESG Climate Solutions to help you gain a better understanding of your exposure to climate-related risks and use the insights to safeguard your investment portfolios.
- Understand the impacts of your investments and how they support the UN Sustainable Development Goals with the ISS ESG SDG Solutions Assessment and SDG Impact Rating.
By:
Gupteswar Satapathy, Research Team Lead – Sustainability Bond Rating
Ria Modh, ESG Methodology Specialist – Regulatory Solutions and Fixed Income
André Noack, ESG Methodology Specialist – Regulatory Solutions and Fixed Income




