Below is an excerpt from ISS-Corporate’s recently released article “Streamlining Sustainability Reporting: Survey Reveals Top Priorities for Corporates”. The full article is available on the ISS-Corporate online library.
Sustainability reporting has become widespread and increasingly complex, as corporate issuers manage stakeholder expectations, regulatory mandates, and alignment with multiple reporting frameworks. As they strive to meet these needs, sustainability reporting teams seek ways to standardize and streamline their approach, ensuring efficiency in data gathering, relevance, accuracy and traceability of sustainability information shared with stakeholders. Software solutions have emerged to address these needs, assisting organizations with data collection, data analysis, and alignment with reporting standards and frameworks.
Survey Overview: Growing Need for Streamlined Reporting
Building on the success of the Celsia reporting platform, ISS-Corporate is expanding its reporting solutions to simplify and improve the efficiency of sustainability reporting. As part of our product development efforts, we conducted a survey among our clients to gather valuable input on the use of reporting tools. The survey explored approaches to sustainability reporting, utilization of reporting frameworks, and desired features in a sustainability reporting software solution. We received responses from 71 corporate issuers, representing companies of all sizes (30% large cap, 41% mid cap, 29% small/micro cap) across all sectors. The geographic distribution was primarily U.S.-based (52 respondents), with a considerable number from Europe (17).
A Multi-Framework Reality
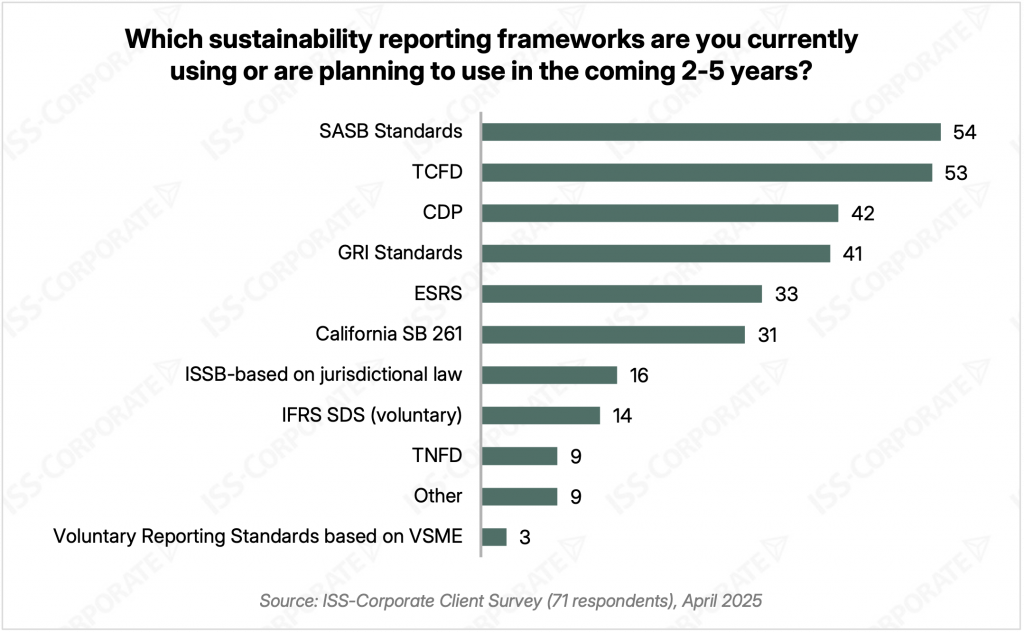
The survey results revealed key insights into the evolving reporting needs of corporate issuers. Regarding reporting standards, an overwhelming 90% of respondents indicated current use or planned adoption of more than one framework, with 79% expressing interest in three or more. Established frameworks, such as the SASB Standards, TCFD, CDP, and GRI, continue to dominate reporting practices. While SASB and TCFD have been incorporated into the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), companies currently reference them as primary. This widespread use suggests likely broader voluntary adoption of the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards issued by the ISSB. Emerging standards driven by regulatory requirements are also prevalent, including California’s Senate Bill 261, requiring climate-related financial risk reporting, aligned with the TCFD framework, and the EU European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), currently under review following the recent EU Omnibus amendment proposal.
By: Kosmas Papadopoulos, Executive Director, Head of Sustainability Advisory – Americas, ISS-Corporate




