The Role of Alliances in Pursuing Net Zero
The Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero (GFANZ), launched in April 2021 at COP26, sought to bring together independent, sector-specific alliances in finance to form a single global coalition for the finance sector. Its mission was to establish a forum to address the unique challenges faced by financial institutions as they attempt to facilitate a global economic transition to Net Zero. Currently, GFANZ and its seven alliances boast over 500 member firms across 50 countries.
In recent months however, GFANZ’s Net Zero Insurance Alliance (NZIA) has experienced an ongoing exodus of its members, raising doubts about its continued existence. Ten insurers, nearly half of the founding members, have left the alliance this year, after political opposition in the U.S. raised concerns over the potential violation of antitrust laws by the NZIA’s stipulated targets and requirements. Insurers appear hesitant to get caught in the crossfire and instead decided to pursue their individual sustainability commitments outside of the coalition. Yet these exits raise the prospect of NZIA’s role being severely diminished, with most of the industry heavyweights gone.
Prior to the NZIA crisis, problems had already begun to surface in another GFANZ alliance, the Net Zero Asset Managers (NZAM) initiative. NZAM took its first blow when a group of major U.S. banks threatened to leave in September 2022. This disruption to GFANZ resulted in a relaxation of criteria for members, as well as the discarding of its previous commitment to the UN’s Race to Zero Campaign.
With companies parting ways with the NZIA, a pattern that might be repeated in other Net Zero-focused finance alliances, an analysis of such alliances may be useful to ESG investors. One question to examine is the effectiveness of these alliances, as their memberships have been often used to identify the Net Zero leaders in the finance industry. Another question is if financial institutions can pursue a Net Zero transition independently of an alliance. ISS ESG Corporate Rating data can illustrate, on a more granular level, how NZIA members have performed against their industry peers.
ESG and Environmental Ratings
This analysis compares the NZIA members (22) at the end of 2022 to all mid- and large-cap insurers (136 above $2 billion market capitalization), through the lens of ISS ESG Corporate Rating’s methodology. Considering all rated members of the NZIA cohort fell in the mid- to large-cap range, small-cap insurers were not considered in this analysis.
More than 77% of the 2022 NZIA members had a sufficiently high ESG performance to receive an overall ‘Prime’ rating by scoring a C (2.00) grade or higher; this overall rating includes Environmental, Social, and Governance aspects. This proportion is significantly higher than that for all mid- and large-cap insurers, where only 29% of companies are Prime (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Proportions of ‘Prime’ Issuers, 2022
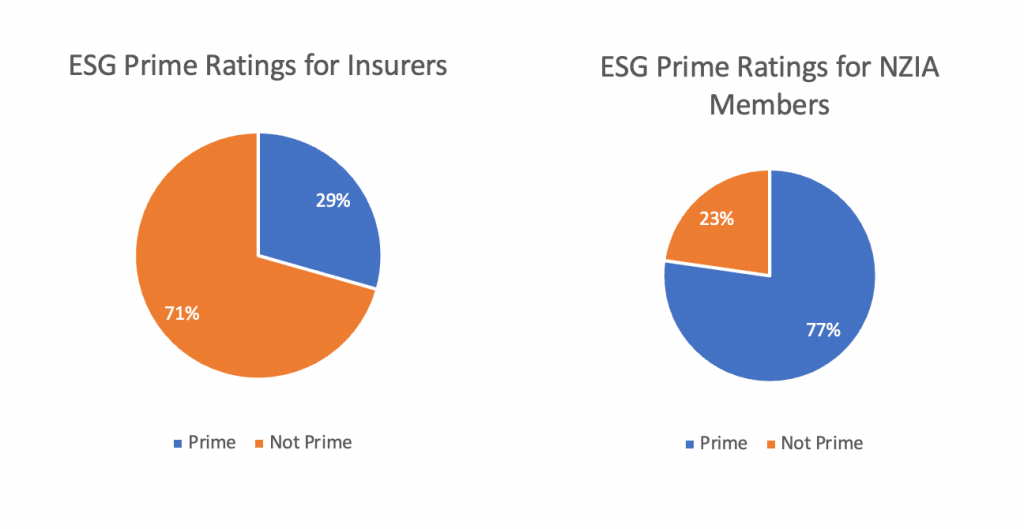
Note: Mid- and large-cap insurers include 136 companies; NZIA members include 22 companies.
Source: ISS ESG
Figure 2 focuses on the Environmental pillar of the overall ESG score, in which respect NZIA members continue to outperform: 55% of them score C or higher, as compared to the industry’s average of just 23% scoring that high.
Figure 2: Environmental Performance Scores of NZIA Insurers Compared to Industry
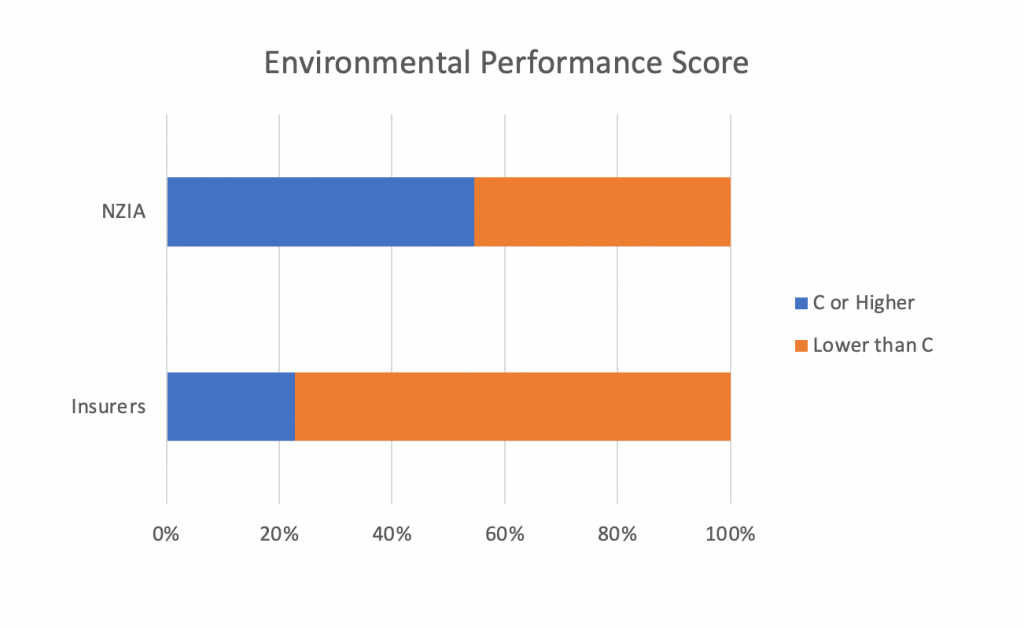
Source: ISS ESG
Half of the top 10 scorers on the numeric scale of this dimension were NZIA members. Insurers are rated on aspects such as the carbon footprint of the portfolio, their monitoring and reporting decarbonization strategy, the environmental guidelines of their underwriting and investment businesses, and their general environmental guidelines for lending and banking.
All the companies that left the NZIA and are covered in the ISS universe had a Prime rating and all except one had an environmental performance score of a C or higher.
Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy
Net Zero ambitions for financial institutions are heavily based on reducing their Scope 3, Category 15 (Investment) emissions, which can constitute up to 99% of their total emissions. Therefore, disclosed commitments and action plans to decarbonize an insurer’s investment and underwriting portfolio are critical for external stakeholders to assess a financial institution’s commitment to Net Zero.
The portfolio decarbonization strategy indicator within the ISS ESG Corporate Rating looks at the mainstreaming of climate considerations across an insurer’s underwriting and investment portfolios, at policies to exclude carbon-intensive activities, and at commitments to finance or insure low-carbon sectors or solutions.
Figure 3 shows that 2022 NZIA members outperformed the industry average, with NZIA members and the insurer industry having scores of 2.25 and 1.60, respectively, for portfolio decarbonization strategy. This is further illustrated by the 2022 NZIA members having a significantly higher proportion (68%) of C or higher-rated entities compared to mid- and large-cap insurers. This means that they have stricter exclusion policies and more comprehensive strategies to mitigate climate change.
Figure 3: Portfolio Decarbonization Strategy and General Environmental Guidelines for Underwriting Performance for NZIA Insurers Compared to the Industry
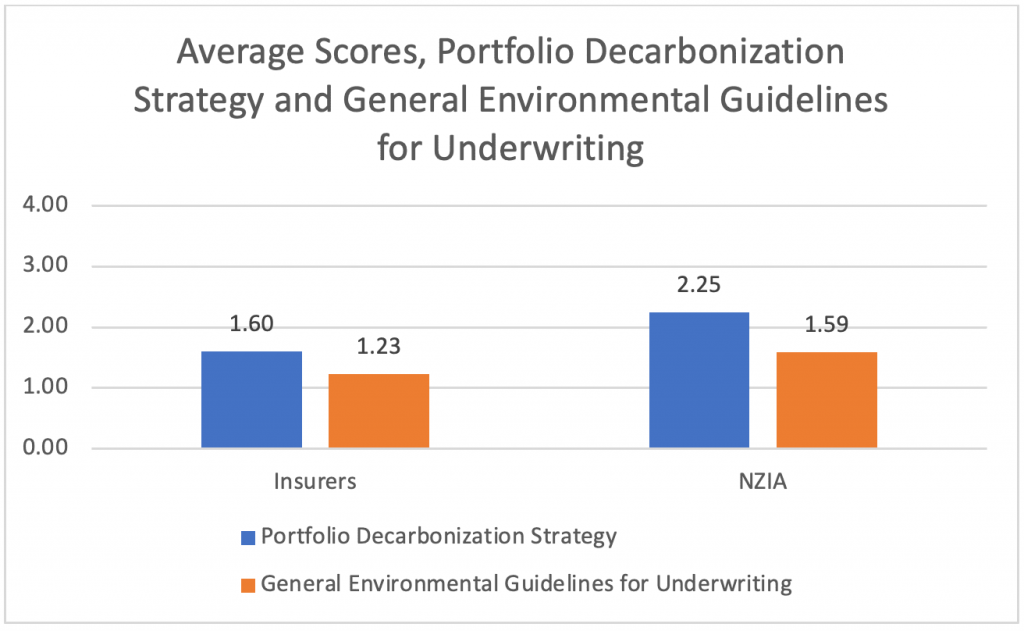
Source: ISS ESG
Among the top 10 scorers for this indicator, half belonged to the 2022 NZIA cohort. Of the 10 companies that have exited the NZIA, the average portfolio decarbonization strategy performance (2.46) surpasses both the industry average (1.60) and 2022 NZIA members (2.25), with only one insurer not receiving a C or higher. Although they are no longer part of the NZIA, the decarbonization strategies of these insurers were among the best in the industry. This suggests that at the end of 2022, the NZIA was made up of the top climate leaders in the insurance sector, with high levels of individual ambition and commitment to decarbonize portfolios already in place. Those insurers that left the alliance are still in a strong position to follow their independent sustainability mandates.
General Environmental Guidelines for Underwriting
Given the nature of their business, insurers can encourage the global transition by implementing general environmental guidelines for underwriting to encourage environmentally sound client behaviour. Crucial to this indicator is the stipulation of underwriting guidelines for clients, across aspects such as the management of environmental risk, resource efficiency, and climate change.
Few companies have such guidelines in place, as reflected by the low average scores for both insurers and 2022 NZIA members shown in Figure 3. Across a total of 89 mid and large-cap insurers who are scored on this indicator, only four achieved a grade of C or higher, and three of them were ex-NZIA members. Of the 10 companies that have exited the NZIA, 42% achieved a grade of C or higher, with a group average of 1.87 (vs. 1.59 for NZIA members and 1.23 for the industry average). Once again, this indicates that the departed members of NZIA were the environmental leaders in their sector.
While general environmental guidelines for underwriting is an important area for insurers to contribute to the global transition, it is also the one of the most poorly scored indicators. This is an area ESG-minded insurers and investors might wish to monitor going forward.
The Effectiveness of the NZIA
Since its inception, the NZIA has worked to develop tools and guidance to help its members set commitments and implement them. On 16 November 2022, the Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials (PCAF) launched the first global standard for insurers to measure and disclose emissions attributable to their underwriting portfolios. This inaugural global standard was developed in collaboration with the NZIA and can help insurers to set targets and track the full range of their financed emissions.
This standard was followed on 17 January 2023 with the publication of NZIA’s Target-Setting Protocol, which guides NZIA members on how to set targets in a consistent manner to achieve Net Zero by 2050. Under ISS ESG’s methodology, an insurer that commits to NZIA’s Target Setting Protocol would improve its scores in both the portfolio decarbonization strategy and general environmental guidelines for underwriting indicators.
ISS ESG’s data indicated that the NZIA cohort at the end of 2022 had some of the most comprehensive strategies and action plans in line with a Net Zero pathway. A company in this cohort was therefore better positioned to reach Net Zero through its portfolio decarbonization strategy, general environmental guidelines for underwriting, and other sustainability standards across all dimensions of ESG.
However, many non-member insurers have also achieved outstanding scores. This suggests the transition might occur within the insurance sector even with a diminished NZIA, as many individual companies have successfully pursued high standards of environmental sustainability independently. In fact, the various sustainability standards of most ex-members were put in place independently of the NZIA, which had only introduced its target-setting protocol this year.
While ex-NZIA members, and other insurers, may continue to raise their standards independently, a strong and successful alliance could arguably generate more decarbonization momentum.
Looking Ahead
The departures from NZIA raise the possibility of a spill-over effect to other GFANZ alliances such as the NZAM; a crucial concern is the possible lowering of standards to try to avoid membership outflows. Such measures call into question the relevance of using memberships as a means of identifying the best-performing companies of the transition.
ISS ESG Corporate Rating can offer a more holistic approach by providing ratings, data, and insights across all three pillars of Environmental, Social, and Governance issues, and by covering an ever-growing group of financial institutions and corporate issuers. Granular information on an individual issuer’s decarbonization efforts and other industry-relevant data are also available for investors and stakeholders to make informed assessments.
Explore ISS ESG solutions mentioned in this report:
- Identify ESG risks and seize investment opportunities with the ISS ESG Corporate Rating.
Authored by:
Nick van Baal, Analyst, Corporate Ratings, Financials, ISS ESG
Jermyn Ng, Associate, Corporate Ratings, Financials, ISS ESG




