Industrial machinery companies’ competitive advantage relies on technological advancement, particularly in providing aftermarket solutions. These services require a closer, more long-term relationship between industrial machinery companies and their clients. Such an enhanced customer focus would allow industrial machinery companies to quickly respond to customer needs and translate innovations into customer-focused solutions.
Data from the ISS ESG Corporate Rating indicates that companies that perform well on aftermarket-relevant indicators also tend to have positive ESG performance. Investors concerned with both the profitability and sustainability of industrial machinery companies may wish to consider the significance of aftermarket services.
Aftermarket Solutions Connected to Returns and Sustainability
Aftermarket solutions for machinery and equipment companies can include spare parts, upgrades and retrofits, repair services, take-back programs, and product training. In recent years, the aftermarket business has also evolved significantly with the adoption of digital tools such as cloud-based predictive maintenance solutions, connected machines, digital twins, and remote sensors.
Aftermarket solutions have proven to offer higher margins than equipment sales, and they are a crucial source of revenue for companies that are reexamining their supply chains in the face of global disruptions. Further, studies have shown that industrial machinery and equipment manufacturers that focus on aftermarket solutions, especially those with a strong digital focus, have delivered higher returns to shareholders.
Aftermarket solutions are also intrinsically linked to a company’s ESG performance. Integrating services at various stages of a product’s lifecycle can play a central role in helping companies reduce their environmental impact and make a more significant contribution to the circular economy. As illustrated in Figure 1, practices such as reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling allow companies to extend the lifecycle of products and consume less energy and materials than they would by producing new products from virgin materials.
Figure 1: Product Lifecycle Extension in a Circular Economy Model
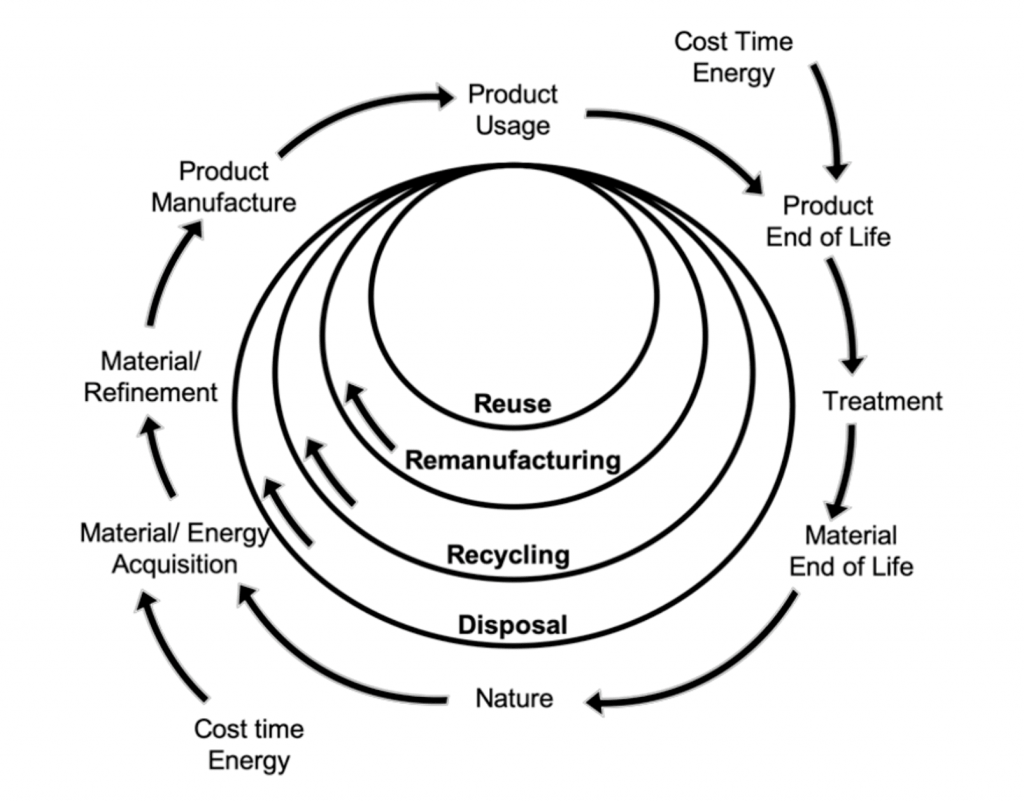
Source: Fontana et al., Circular Economy Strategies for Equipment Lifetime Extension: A Systematic Review, Sustainability (2021) 13 (3): 1117
Companies seeking to stay ahead of their competitors can not only assume the responsibility of improving their organization’s sustainability performance but also proactively support customers to achieve their sustainability goals.
For example, machinery and equipment manufacturers that offer take-back and recycling initiatives as well as remanufacturing services reduce the need for new resources and help customers to improve recycling efforts and waste reduction initiatives. Additionally, by offering product upgrades and options for modernization, companies can help customers optimize the energy efficiency of their equipment, thereby supporting their carbon reduction efforts. Moreover, the provision of preventive maintenance and remote monitoring plays a crucial role not only in minimizing the risks of injuries during the use phase of products but in reducing machinery downtime and thus resource use.
Overall, by supporting customers throughout a product’s entire lifecycle, industrial machinery manufacturers can better contribute to sustainable development goals and foster strong customer relationships, resulting in a positive brand reputation.
Aftermarket Solutions and ESG Performance in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment Industry
The ISS ESG Corporate Rating adopts an industry-specific approach, emphasizing key sustainability concerns and opportunities within each industry. To ensure that a company’s performance on the most material issues specific to each industry is adequately reflected in the overall rating results, the cumulative weighting of these key sustainability issues accounts for at least 50 percent of the overall rating.
For companies operating in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment industry, half of the key sustainability issues are closely linked to products, covering issues such as product safety and the environmental performance of products. The ESG performance assessment incorporates aspects including customer support and protection, product lifecycle, material efficiency, and product energy efficiency. Notably, these key issues are integral components of aftermarket offerings, which means that a company’s approach to these key issues can, in turn, reflect how a company’s corporate culture prioritizes longer-term client relationships.
Table 1 shows the minimum, maximum, and average scores the Top 10 and Bottom 10 ESG performers in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment industry receive on key sustainability issues. The Top 10 ESG performers fare better, on average, on each of the key metrics compared to the Bottom 10 companies. For indicators such as product lifecycle and energy efficiency of products, the minimum scores Top 10 companies received are higher than the maximum scores received by any of the Bottom 10 companies on these same indicators.
Table 1: Minimum, Maximum, and Average Performance Scores of the Top 10 and Bottom 10 Industrial Machinery and Equipment ESG Performers on Key Sustainability Issues
Top 10 ESG Performers in Industrial Machinery and Equipment
| Key Issues | Minimum Score | Maximum Score | Average Score |
| Customer support and protection | 1.80 | 3.70 | 2.69 |
| Product lifecycle | 2.13 | 2.88 | 2.38 |
| Material efficiency | 1.63 | 2.68 | 2.09 |
| Energy efficiency of products | 2.25 | 3.33 | 2.78 |
Bottom 10 ESG Performers in Industrial Machinery and Equipment
| Key Issues | Minimum Score | Maximum Score | Average Score |
| Customer support and protection | 1.00 | 2.30 | 1.26 |
| Product lifecycle | 1.00 | 1.22 | 1.11 |
| Material efficiency | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.06 |
| Energy efficiency of products | 1.00 | 1.75 | 1.12 |
Source: ISS ESG Corporate Rating
As Figure 2 indicates, ESG leaders in the industry (those with a Prime score, or C+ and above, for their overall ESG performance) significantly outperform laggards (those with a grade of D+ and below for their overall ESG performance) on the aftermarket-related indicators of Environmental Performance of Products and Product Safety.
Figure 2: Distribution of Scores for Overall ESG Leaders and Laggards in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment Industry on Environmental Performance of Products and Product Safety Indicators
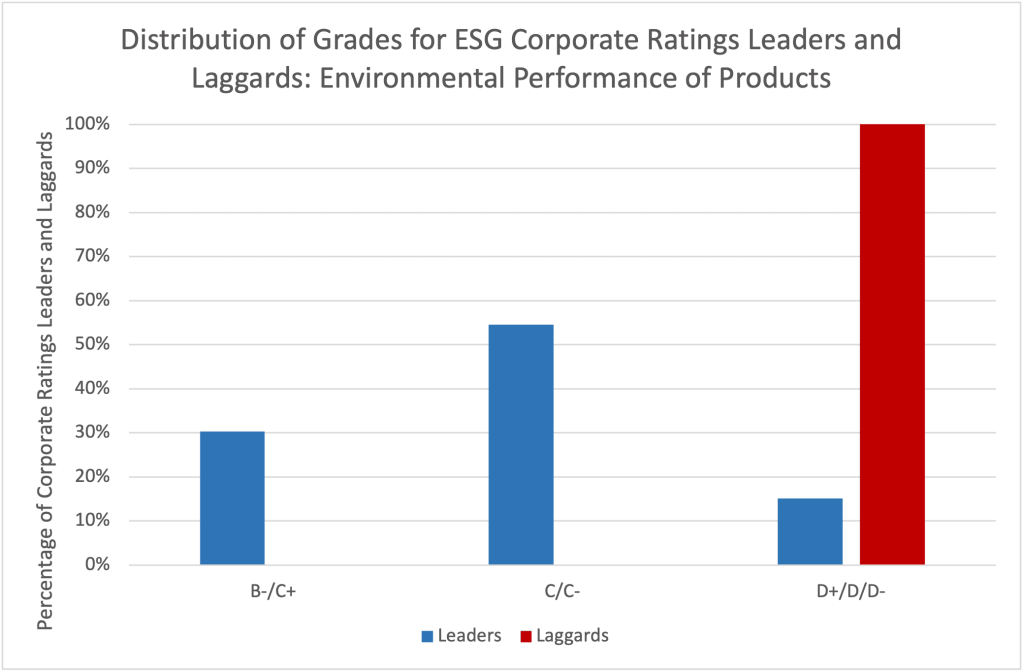
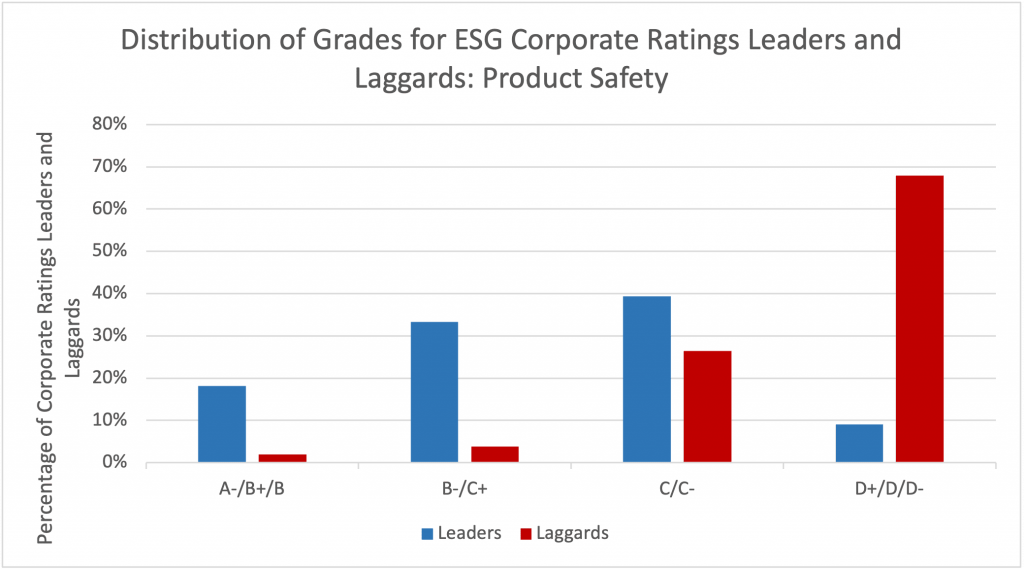
Notes: Leaders = Companies rated Prime (C+ and above) on their overall ESG performance; Laggards = D+/D/D- on their overall ESG performance.
Source: ISS ESG Corporate Rating
Aftermarket services can also enhance company revenue and improve sales margins drastically. In fact, the average of aftermarket as a percentage of total sales for the top 10 ESG performers in ISS’s Industrial Machinery and Equipment industry is more than double that of the bottom 10 performers.
Nevertheless, the overall performance of Industrial Machinery and Equipment companies concerning aftermarket-related ESG issues is relatively low, with average grades ranging from D- to C- (Figure 3). Most companies are proactive about providing aftermarket services to customers and have implemented some measures to ensure product safety and product energy efficiency.
Figure 3: Distribution of Grades Assessing Industrial Machinery and Equipment Companies’ Performance on Key ESG Topics Associated with Products
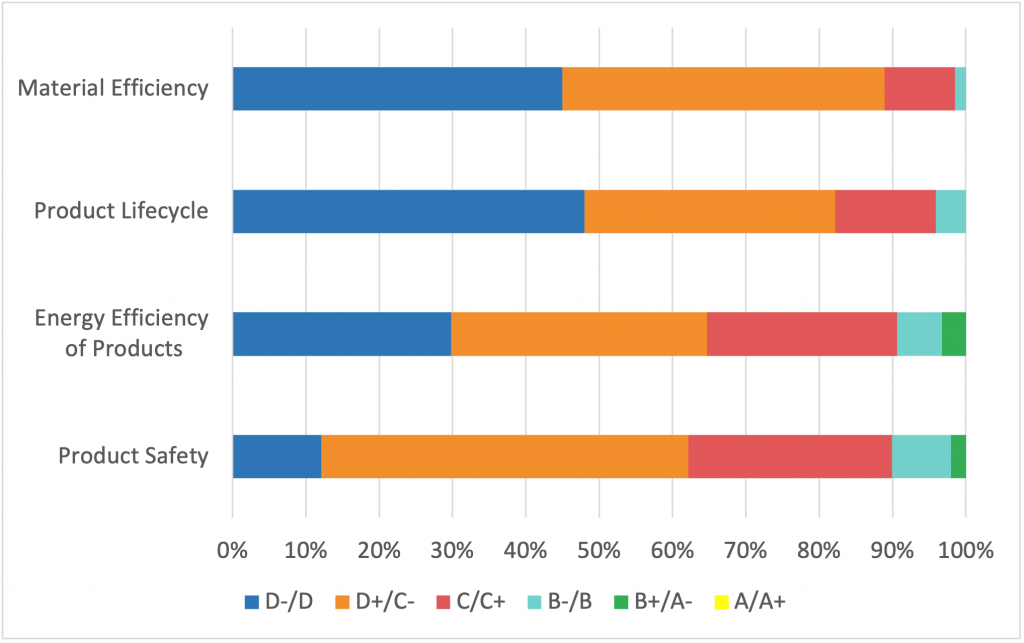
Source: ISS ESG Corporate Rating
However, fewer than 10 percent of companies achieve a grade above B in all four areas, which suggests that most companies have yet to harness the potential of aftermarket solutions, despite their vital role in addressing key sustainability issues associated with products.
ESG and EVA Performance in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment Industry
Beyond benefits such as higher margins and customer loyalty, aftermarket solutions offer investors the prospect of a link to strong ESG performance. Companies with robust aftermarket offerings tend to be ESG outperformers: data from the ISS ESG Corporate Rating indicates that ESG leaders consistently achieve higher scores on product sustainability-related indicators compared to laggards.
While ESG performance data provides valuable insights into a company’s commitment to sustainability, investors can assess a company’s potential for delivering strong returns through the lens of ISS Economic Value Added (EVA). EVA Margin, a measure of a company’s financial profitability after accounting for all operating expenses, taxes, and capital charges, can be used to gauge a company’s economic profitability. Investors may consider using EVA Margin data in conjunction with other key financial metrics, such as Return on Investment (ROI) and Return on Equity (ROE), for a more complete analysis of a company or investment.
Figure 4 compares ESG leaders, medium performers, and laggards based on their average EVA Margin, ROI, and ROE. It is evident that ESG leaders in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment industry exhibit higher EVA Margin, ROI, and ROE on average compared to their peers. This indicates a positive correlation between ESG performance and financial profitability, further highlighting that aftermarket solutions could be connected to financial profitability.
Figure 4: Average EVA Margin, Return on Investment, and Return on Equity of ESG Leaders, Medium Performers, and Laggards in the Industrial Machinery and Equipment Industry
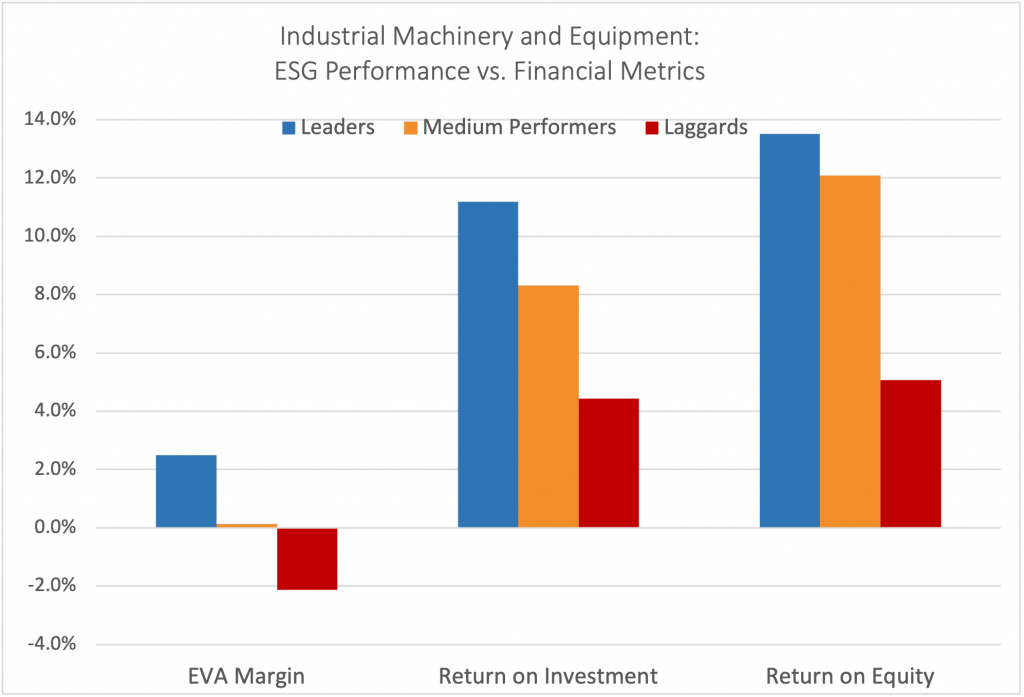
Notes: Data covers 193 companies within the Industrial Machinery and Equipment industry. Leaders = Companies rated Prime (C+ and above); Medium Performers = C/C-; Laggards = D+/D/D-. A higher percentage reflects a higher EVA Margin, Return on Investment, or Return on Equity value.
Source: ISS ESG Corporate Rating and ISS EVA
Conclusion
Embracing a comprehensive aftermarket strategy is not just an afterthought for industrial machinery companies, but a critical step towards a sustainable and profitable future. In light of these insights, investors should be cognizant of the risks and opportunities associated with the service aspect of industrial machinery companies’ business strategies. Evaluating how companies integrate ESG factors within aftermarket solutions can yield valuable insights into their commitment to responsible business practices and their potential for sustainable economic growth.
Explore ISS ESG solutions mentioned in this report:
- Identify ESG risks and seize investment opportunities with the ISS ESG Corporate Rating.
- Understand the F in ESGF using the ISS EVA solution.
By: Amanda Gan, Corporate Ratings Associate
Sophia Iosue, Corporate Ratings Associate